“Home insurance
Artikel Terkait Home insurance
- Home Insurance Premium
- Home Insurance Claim
- Types Of Home Insurance
- Home Insurance Policy
- Tips For Choosing Home Insurance
Pengantar
Dengan senang hati kami akan menjelajahi topik menarik yang terkait dengan Home insurance. Mari kita merajut informasi yang menarik dan memberikan pandangan baru kepada pembaca.
Table of Content
Video tentang Home insurance
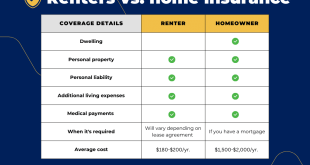
Home insurance, also known as homeowner’s insurance, is a type of property insurance that covers losses and damages to your home and its contents. It provides financial protection against unforeseen events such as fire, theft, vandalism, and natural disasters. Understanding the intricacies of home insurance is essential for every homeowner to ensure they have adequate coverage and peace of mind.

What Does Home Insurance Cover?
A standard home insurance policy typically includes several key coverages:
-
Dwelling Coverage: This covers the physical structure of your home, including the walls, roof, foundation, and attached structures like garages and porches. It protects against damage from covered perils, such as fire, windstorms, hail, and lightning. The coverage amount is usually based on the replacement cost of your home, not its market value.
-
Other Structures Coverage: This covers detached structures on your property, such as a shed, fence, or detached garage. The coverage amount is typically a percentage of your dwelling coverage.
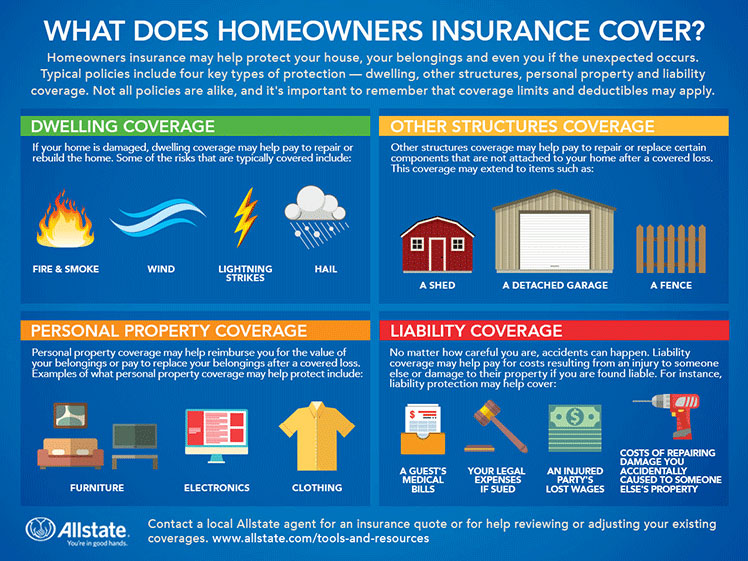
Personal Property Coverage: This covers your belongings inside your home, including furniture, clothing, electronics, and jewelry. Coverage is usually provided on an actual cash value (ACV) basis, meaning the payout will reflect the item’s current value, minus depreciation. Some policies offer replacement cost coverage, which covers the cost of replacing the item with a new one.
-
Loss of Use Coverage: This covers additional living expenses if your home becomes uninhabitable due to a covered loss. This can include hotel bills, temporary housing costs, and other expenses incurred while your home is being repaired or rebuilt.
-
Personal Liability Coverage: This protects you from financial liability if someone is injured on your property or if you are legally responsible for damage to someone else’s property. This coverage typically includes legal defense costs.
-
Medical Payments Coverage: This covers medical expenses for guests or others who are injured on your property, regardless of whether you are at fault.


Types of Home Insurance Policies
Several types of home insurance policies cater to different needs and circumstances:
-
HO-3 (Special Form): This is the most common type of homeowner’s insurance policy. It provides open-peril coverage for your dwelling and other structures, meaning it covers damage from almost any cause except those specifically excluded in the policy. Personal property is covered for named perils, meaning it only covers damage from specific events listed in the policy.
-
HO-5 (Comprehensive Form): This policy provides open-peril coverage for both your dwelling and personal property. It offers the broadest coverage available.
-
HO-4 (Renters Insurance): This policy is designed for renters and covers their personal belongings and liability. It does not cover the building itself.
-
HO-6 (Condominium Insurance): This policy is specifically designed for condominium owners. It covers the interior of the condo unit and personal belongings, but it does not cover the building’s common areas.
-
HO-8 (Modified Coverage Form): This policy is typically used for older homes that are difficult to insure due to their age or condition. It provides more limited coverage than other policies.
Factors Affecting Home Insurance Premiums
Several factors influence the cost of your home insurance premiums:
-
Location: Your home’s location plays a significant role in determining your premiums. Homes in areas prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, or wildfires, will generally have higher premiums.
-
Home Value: The higher the value of your home, the higher your premiums will likely be.
-
Coverage Amount: The amount of coverage you choose will directly impact your premium. Higher coverage amounts mean higher premiums.
-
Deductible: Your deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. A higher deductible will result in lower premiums, but you’ll have to pay more in the event of a claim.
-
Credit Score: In many states, your credit score is a factor in determining your insurance premiums. A higher credit score can lead to lower premiums.
-
Claims History: A history of filing insurance claims can lead to higher premiums.
-
Home Features: Certain home features, such as a security system or fire sprinklers, can lower your premiums.
-
Insurance Company: Different insurance companies have different pricing structures. Comparing quotes from multiple insurers is crucial to finding the best rate.
Choosing the Right Home Insurance Policy
Selecting the appropriate home insurance policy requires careful consideration of your individual needs and circumstances. Here are some key steps to follow:
-
Assess Your Needs: Determine the value of your home and its contents. Consider the potential risks in your area and the level of coverage you require.
-
Compare Quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple insurance companies to compare coverage options and prices. Don’t just focus on price; compare the coverage provided.
-
Review the Policy: Carefully review the policy documents before signing. Understand the coverage details, exclusions, and limitations.
-
Consider Additional Coverage: Think about adding optional coverage, such as flood insurance, earthquake insurance, or personal umbrella liability insurance, depending on your risk profile and location.
-
Update Your Policy Regularly: As your home’s value increases or your possessions change, ensure your coverage remains adequate. Update your policy accordingly.
Common Exclusions in Home Insurance Policies
It’s important to understand what your home insurance policy does not cover. Common exclusions include:
-
Flooding: Flood insurance is typically a separate policy and is not included in standard homeowner’s insurance.
-
Earthquakes: Earthquake insurance is also usually a separate policy.
-
Acts of War: Damage caused by war or other acts of terrorism is typically excluded.
-
Neglect or Intentional Damage: Damage caused by negligence or intentional acts is generally not covered.
-
Normal Wear and Tear: Routine maintenance and repairs are not covered.
Filing a Home Insurance Claim
If you need to file a claim, follow these steps:
-
Contact Your Insurance Company: Report the damage to your insurance company as soon as possible.
-
Document the Damage: Take photos and videos of the damage. Keep records of all expenses related to the damage.
-
Cooperate with the Adjuster: An insurance adjuster will investigate the claim and assess the damage. Cooperate fully with their investigation.
-
Follow the Claim Process: Follow your insurance company’s procedures for filing a claim.
Conclusion
Home insurance is a vital financial tool for protecting your most valuable asset. Understanding the different types of policies, coverage options, and factors that affect premiums is crucial for making informed decisions. By carefully considering your needs and comparing quotes from multiple insurers, you can ensure you have adequate protection and peace of mind. Remember to regularly review and update your policy to reflect changes in your circumstances. Don’t hesitate to contact your insurance agent or company if you have any questions or need clarification on your policy’s coverage. Protecting your home is an investment in your future security and financial well-being.

Penutup
Dengan demikian, kami berharap artikel ini telah memberikan wawasan yang berharga tentang Home insurance. Kami berterima kasih atas perhatian Anda terhadap artikel kami. Sampai jumpa di artikel kami selanjutnya!
 seeme
seeme